Pumping solar systems
A solar-powered water pumping system (SPWPS) is a standalone solution that utilizes solar energy to pump water from sources such as wells, boreholes, rivers, or tanks for various applications including agriculture, livestock, domestic use, and irrigation. These systems are especially valuable in remote or off-grid areas where access to electricity is limited or non-existent.
The global demand for sustainable water pumping solutions is increasing due to growing water scarcity, the rising cost of fossil fuels, and the push for decarbonization in rural infrastructure. Traditional water pumping systems, particularly those powered by diesel generators, are not only expensive to operate and maintain but also contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Solar-powered water pumping systems (SPWPS) present an effective, environmentally friendly alternative, particularly suited for off-grid or low-resource settings. The integration of photovoltaic (PV) technology into irrigation and water supply systems has the potential to transform agricultural productivity, reduce energy poverty, and enhance climate adaptation measures.
Key components:
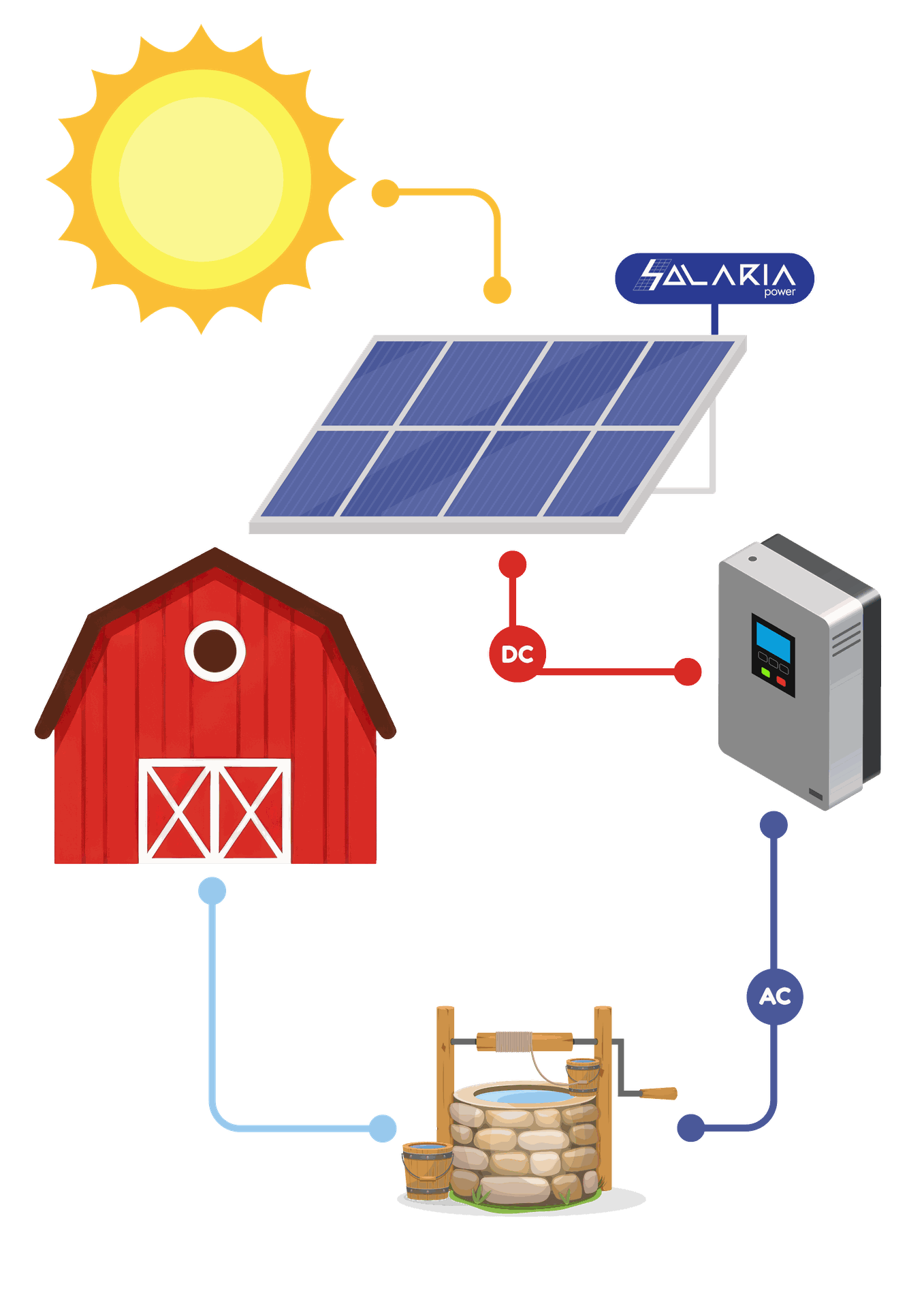
Photovoltaic (PV) Array: Converts solar energy into direct current (DC) electricity. The size of the PV array depends on the daily water requirement, solar insolation levels, and the depth of the water table.
Pump Controller or Inverter: Manages power flow between the PV array and the pump motor. In DC systems, a controller optimizes voltage levels and protects the pump from dry running. In AC systems, an inverter converts DC power to alternating current (AC) suitable for standard pump motors.
Electric Motor and Pump: Can be submersible (used for deep wells) or surface-mounted (used for shallow water sources). The motor type (DC or AC) is selected based on system size and energy availability.
Water Storage System (Optional): To compensate for intermittent solar availability, many systems include elevated storage tanks that store water during sunlight hours for use during non-productive periods.
Here is a simplified illustration for the Pumping solar system:
Advantages:
Renewable and Clean Energy Source: Solar pumps do not emit greenhouse gases and significantly reduce the carbon footprint compared to diesel alternatives.
Low Operational Costs: After the initial capital investment, solar pumps incur minimal operating and maintenance costs.
Scalability and Modularity: Systems can be designed for small family farms or scaled up for commercial irrigation projects.
Independence from Grid Infrastructure: Ideal for rural or isolated regions where grid extension is economically infeasible.
Water-Energy Nexus Alignment: Contributes to sustainable resource management by simultaneously addressing water and energy access.
Applications:
Agricultural Irrigation: Solar pumping enables drip or sprinkler irrigation in remote areas, reducing dependence on rain-fed agriculture and increasing crop yields.
Livestock Watering: Provides reliable water supply for animal husbandry in remote pastures.
Domestic Water Supply: Used in rural villages to provide drinking water and sanitation through borehole pumping systems.
Aquaculture and Fisheries: Facilitates pond filling, aeration, and water circulation systems.