Off-grid solar systems
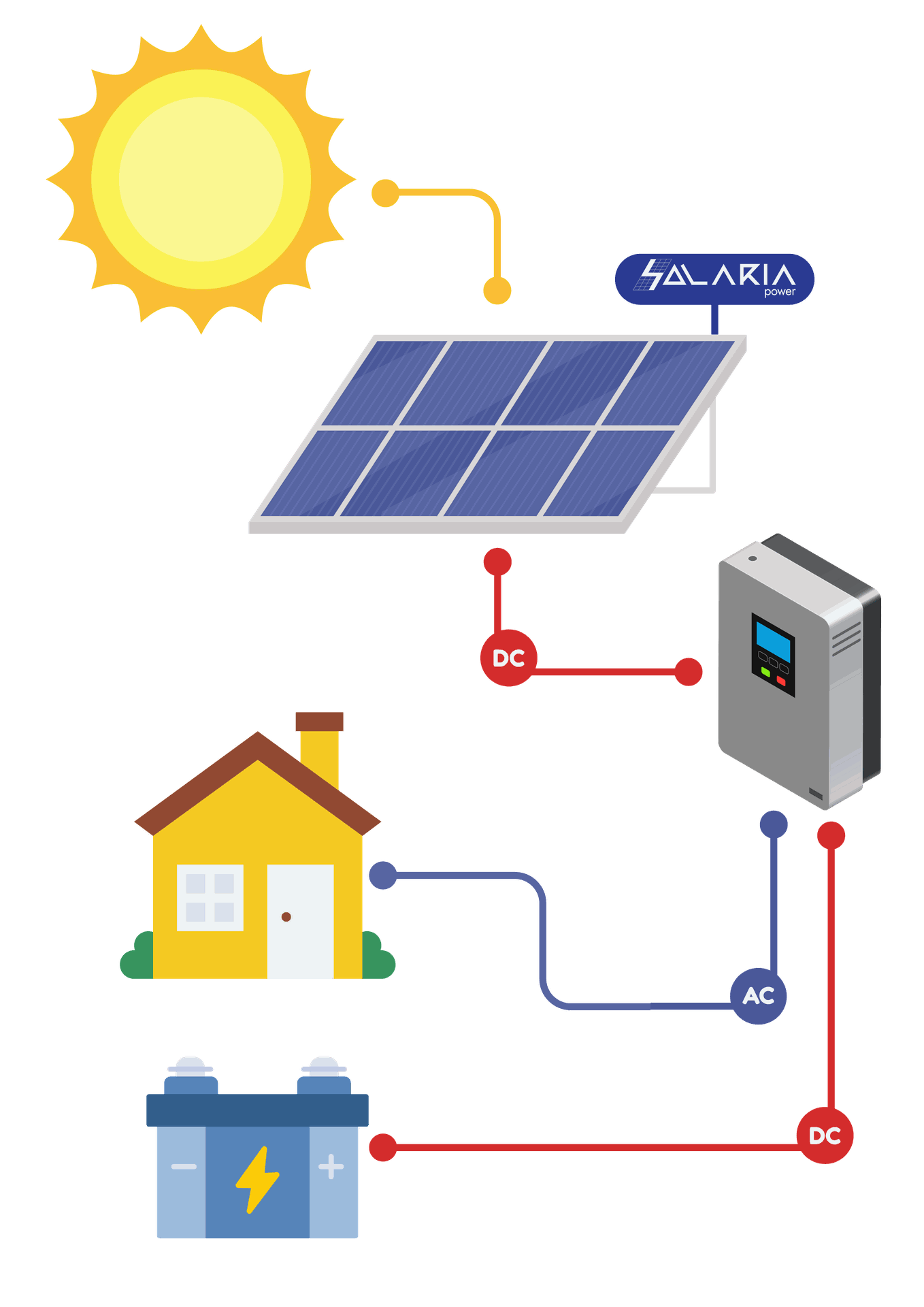
An off-grid solar system, also referred to as a stand-alone photovoltaic system, operates independently of the utility grid. It is designed to generate, store, and distribute electricity autonomously, making it particularly suitable for rural electrification, agricultural use, and disaster-relief operations. The system typically comprises solar panels, charge controllers, battery storage units, and inverters.
As global energy demand increases and concerns regarding environmental sustainability intensify, renewable energy systems have emerged as critical alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based energy generation. Among these, solar photovoltaic (PV) systems have gained considerable attention due to their scalability, declining costs, and adaptability to diverse environments. Off-grid solar systems, in particular, offer a reliable power source in areas where access to the national electricity grid is limited or economically unfeasible.
Key components:
Solar Panels: These are responsible for converting sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity using the photovoltaic effect. Panel efficiency and orientation significantly influence system performance.
Charge Controller: This device regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to prevent overcharging or deep discharging of the battery bank, thus extending battery lifespan.
Battery Bank: Energy storage is critical in off-grid systems to ensure energy availability during periods of low solar irradiance or at night. Common battery types include lead-acid and lithium-ion.
Inverter: Converts stored DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used by most household appliances and equipment.
Here is a simplified illustration for the Off-grid solar system:
Advantages:
Energy Independence: Users are not subject to grid failures, voltage fluctuations, or utility pricing.
Accessibility: Enables electrification of remote and underserved areas without costly grid extensions.
Environmental Impact: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
Scalability: Systems can be designed for a range of applications, from small-scale lighting to powering entire villages.
Applications:
Rural Electrification: Providing basic lighting and power in off-grid villages.
Agricultural Sector: Powering irrigation systems, water pumps, and cold storage.
Emergency Response: Supporting medical and communication equipment in disaster-affected zones.
Tourism and Eco-Lodges: Offering sustainable energy solutions in remote destinations.